

Higher and foundation tiers
 Carbon dioxide is a colourless odourless gas. It is produced mainly in the science lab by the reaction of
metal carbonates with
acids.
To test for carbon dioxide gas uses a limewater (calcium hydroxide) solution.
Carbon dioxide gas will turn a
limewater solution milky or chalky in colour. Limewater is an
alkaline
solution and carbon dioxide is an acidic gas. The
carbon dioxide gas reacts with the limewater solution to produce a cloudy suspension of
calcium carbonate which is responsible for the milky or chalky colour.
Carbon dioxide is a colourless odourless gas. It is produced mainly in the science lab by the reaction of
metal carbonates with
acids.
To test for carbon dioxide gas uses a limewater (calcium hydroxide) solution.
Carbon dioxide gas will turn a
limewater solution milky or chalky in colour. Limewater is an
alkaline
solution and carbon dioxide is an acidic gas. The
carbon dioxide gas reacts with the limewater solution to produce a cloudy suspension of
calcium carbonate which is responsible for the milky or chalky colour.
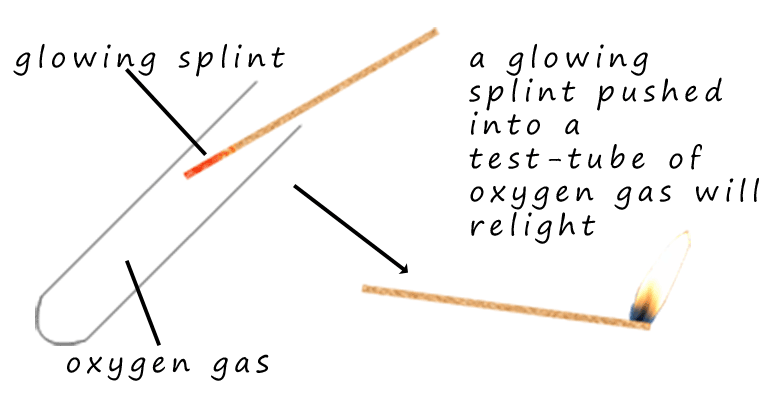 Oxygen gas is needed for burning
or combustion. In air if a burning splint is blown out but the
end still glows it will not relight, however if a glowing splint is pushed into a test-tube containing pure
oxygen gas it immediately bursts back into flame.
Oxygen gas is needed for burning
or combustion. In air if a burning splint is blown out but the
end still glows it will not relight, however if a glowing splint is pushed into a test-tube containing pure
oxygen gas it immediately bursts back into flame.
 Chlorine gas will bleach damp litmus paper white. The litmus paper may turn red
at first but
this will quickly fade. Chlorine dissolves in the water on the damp litmus paper to form an acid;
this explains why it initially turns red.
Chlorine gas will bleach damp litmus paper white. The litmus paper may turn red
at first but
this will quickly fade. Chlorine dissolves in the water on the damp litmus paper to form an acid;
this explains why it initially turns red.
 Mixtures of hydrogen and oxygen gases are explosive.
This explosion is used to test for the presence of hydrogen gas. If a burning splint is placed just above the mouth of a test-tube containing
hydrogen gas then a squeaky pop will be heard as the
hydrogen gas explodes in air.
Mixtures of hydrogen and oxygen gases are explosive.
This explosion is used to test for the presence of hydrogen gas. If a burning splint is placed just above the mouth of a test-tube containing
hydrogen gas then a squeaky pop will be heard as the
hydrogen gas explodes in air.